IT asset lifecycle management: The complete guide for 2026
 GroWrk Team
GroWrk Team
Losing track of company laptops? Constantly overspending on software licenses you don’t use? You’re not alone. The chaos of managing technology assets can lead to cost overruns, security vulnerabilities, and lost productivity. The solution is a strategic process called IT Asset Lifecycle Management (ITALM), which provides a structured approach to managing asset lifecycles, optimizing costs, and making decisions.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know. We’ll cover what ITALM is, why it’s important, the 5 stages of the asset lifecycle, and the best tools to help you get in control. Digital transformation is driving the need for more advanced ITALM solutions, making it essential for all organizations, including medium-sized businesses, to have a scalable, effective asset management strategy. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to transform your IT from chaotic and reactive to strategic and efficient.
What is IT Asset Lifecycle Management (ITALM)?
.jpg?width=600&height=300&name=IT%20asset%20lifecycle%20management%20The%20complete%20guide%20(1).jpg)
IT Asset Lifecycle Management is the process of tracking, managing, and optimizing all of your company’s technology assets from the moment they are requested and purchased to the moment they are securely disposed of. ITALM systems aggregate asset information from multiple sources to create a single, searchable database. An “IT asset” isn’t just a laptop or a server; it includes:
-
Hardware: Desktops, laptops, mobile devices, servers, network equipment.
-
Software: Licensed applications, subscriptions (SaaS), operating systems.
-
Cloud Assets: Virtual machines, cloud storage, other digital infrastructure.
-
Peripherals: Monitors, keyboards, printers, other connected devices.
-
Other assets: Additional peripherals and virtual resources that are important for inventory management.
A robust ITLAM strategy provides a single source of truth for your entire tech inventory so you can make better financial, operational and security decisions.
Why ITALM is non-negotiable for your business in 2026
Managing your IT assets isn’t just about tidiness; it’s a business function that delivers results. ITALM simplifies business processes across the organization, enabling greater control and efficiency. The complexity of modern IT infrastructure, from remote work setups to sprawling cloud services, makes manual tracking in spreadsheets impossible. Here’s why a formal ITALM program is essential. Automated workflows in ITALM platforms simplify IT services management, making support processes and service delivery more seamless.
Drastic cost savings
Without visibility of your assets, you’re wasting money. ITALM helps you:
-
Eliminate “ghost assets”: Stop paying for software licenses or maintenance on equipment that’s lost, stolen, or no longer in use. By identifying and retiring underperforming assets, ITALM reduces maintenance costs.
-
Optimize software licenses: Avoid over-purchasing licenses by reallocating unused ones and ensuring you’re compliant to avoid hefty fines.
-
Better budgeting: Make informed purchasing decisions based on actual usage data and future needs, not guesswork. Optimizing asset usage can increase productivity across the organization.
Enhanced security and compliance
Unmanaged assets are open doors for security threats. ITALM is your first line of defense.
-
Close security gaps: Ensure every device is properly configured, patched with the latest security updates, and monitored for risks. ITALM also supports risk management by identifying compliance and security risks proactively so you can prevent issues before they arise.
-
Ensure compliance: Easily prove compliance with industry regulations (like GDPR or HIPAA) and software licensing agreements by having accurate records.
-
Secure data disposal: Implement standardized processes to wipe sensitive company data from devices before they’re recycled, resold, or disposed of.
Increased operational efficiency
A well-oiled ITALM program simplifies processes across your organization.
-
Faster onboarding: Deploy the right hardware and software to new employees, get them productive from day one.
-
Reduced downtime: Proactively manage and maintain equipment to prevent unexpected failures, and use data to predict when an asset needs repair or replacement.
-
Simplified IT support: The IT department, as the primary user of ITALM tools, can optimize support processes by having access to asset data. This enables better decision-making, as the IT department knows the exact configuration, location, and history of every asset, allowing them to resolve issues faster.
The 5 phases of the IT asset lifecycle
.jpg?width=600&height=300&name=IT%20asset%20lifecycle%20management%20The%20complete%20guide%20(6).jpg)
The IT asset lifecycle provides a structured framework for managing an asset from start to finish. The process begins with the planning stage, where needs are assessed and strategic decisions are made. Understanding these 5 stages is key to building an ITALM strategy.
Phase 1: Procurement & planning
This is where it all begins. It’s not just about buying new things; it’s about making strategic decisions.
-
Needs assessment: What assets do you really need to meet business goals? Use digital twin technology to simulate asset performance and inform purchasing decisions, enabling you to choose the right asset.
-
Inventory audit: Check your current inventory to see if an existing asset can be repurposed before buying a new one.
-
Budgeting: Allocate funds based on a clear understanding of costs, including purchase price, maintenance, and support over the asset’s lifetime.
- Assessment: Consider the following when choosing suppliers: scalability, integration, and compliance, as these are key to efficient asset lifecycle management.
-
Supplier selection: Research and select suppliers who offer the best value and meet your company’s standards.
Phase 2: Deployment
Once an asset is purchased, it needs to be properly introduced into your environment.
-
Configuration & installation: Set up the hardware or software according to company security policies and user requirements, including cloud-based assets and virtual infrastructure.
-
Inventory tagging: Add the new asset to your central ITALM database or software, recording key details like serial number, owner, location, and purchase date.
-
User training: Ensure the employee receiving the asset knows how to use it effectively and securely.
Phase 3: Management & maintenance
This is the longest stage during which the asset is used to deliver value. The goal is to maximize performance and lifespan.
-
Tracking & monitoring: Continuously track the asset’s location, condition, and usage. This includes monitoring software for updates and patches. Monitoring the asset’s performance is key to informing maintenance decisions and proactively repairing assets before they fail.
-
Preventive maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance (e.g., system cleanups, hardware checks) to prevent failures before they happen. Scheduling and documenting asset maintenance and maintenance tasks helps extend asset lifespan, reduce downtime, and increase operational efficiency.
-
Predictive maintenance: For critical systems, use data and AI tools to predict when a component will fail so you can address it before it does. AI-driven parts management can optimize spare parts inventory so that necessary components are available for timely repairs and maintenance.
Phase 4: Support
Throughout its life, an asset will require support to keep it running smoothly and productively for the user.
-
Helpdesk & troubleshooting: Provide technical support to users to resolve issues, manage repairs, and handle warranty claims. Manual support processes can be time-consuming, but ITALM tools can automate and streamline these tasks.
-
Upgrades: Manage hardware component upgrades or software version updates to extend the asset’s life and enhance its capabilities.
Phase 5: Retirement & disposal
Every asset will eventually reach the end of its life. This final stage must be handled carefully to protect data and minimize environmental impact.
-
End-of-life decision: Decide when an asset is no longer cost-effective to maintain or when it no longer meets performance needs.
-
Data sanitization: Wipe all sensitive information from the asset according to industry standards.
-
Disposal: Choose a responsible disposal method, such as recycling through a certified e-waste partner, reselling to recover residual value, or donating to a charitable organization. Recycling, reselling, or donating old equipment helps organizations meet sustainability and ESG goals and ensures proper documentation, like disposal certificates. Proper disposal is especially important for on-premises assets to maintain compliance and data security. Using a single platform to manage asset retirement and disposal simplifies the process across all asset types, improving oversight and efficiency.
Asset tracking and monitoring: Keeping tabs on every asset
.jpg?width=600&height=300&name=IT%20asset%20lifecycle%20management%20The%20complete%20guide%20(3).jpg)
Asset tracking and monitoring form the foundation of an effective asset management strategy. By maintaining real-time visibility across the entire asset lifecycle, organizations can improve asset performance, reduce downtime, and boost operational efficiency. Modern tools, such as computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) or asset management software, simplify the asset management process and help teams make faster, data-driven decisions.
Key advantages of asset tracking and monitoring include:
-
Real-time visibility: Track assets across locations and monitor asset health to quickly address performance issues.
-
Preventive maintenance: Identify problems early and schedule maintenance before costly repairs are needed.
-
Improved asset utilization: Optimize how assets are used to extend their lifespan and reduce unnecessary maintenance costs.
-
Centralized management: Manage all data within a single system like CMMS for easier reporting and oversight.
-
Software compliance: Keep software licenses current and support effective software asset management.
-
Data-driven insights: Analyze asset information to spot trends, manage risks, and guide better decision making.
By integrating asset tracking into your asset management process, your organization can enhance reliability, control maintenance costs, and ensure every asset performs effectively throughout its lifecycle management.
Leveraging artificial intelligence in ITALM
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are redefining how organizations manage and optimize assets. When integrated into asset management software, these technologies provide smarter automation, predictive insights, and improved asset performance across the entire asset lifecycle.
Key ways AI and ML enhance asset management include:
-
Predictive analytics: Use AI-driven models to detect performance patterns, forecast failures, and schedule preventive maintenance before issues escalate.
-
Automated workflows: Streamline routine tasks like tracking software licenses, monitoring asset health, and generating compliance reports.
-
Customizable dashboards: Leverage advanced analytics to visualize asset utilization, potential risks, and overall asset reliability.
-
Smarter decision-making: Combine AI insights with asset data to align actions with business goals and reduce downtime or maintenance costs.
-
Operational efficiency: Free IT teams from repetitive work so they can focus on strategy, innovation, and lifecycle management improvements.
By leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning, organizations can boost asset reliability, extend asset lifespan, and make better data-driven decisions that strengthen their overall asset management strategy.
The best IT Asset Lifecycle Management tools for 2026
While the process is clear, managing it all manually is a recipe for failure. Modern ITALM software automates tracking and provides the data-driven insights you need to succeed. An integrated solution combines IT asset management, service management, and lifecycle management in one platform, enabling seamless collaboration and improved efficiency.
Key Features to Look for in ITALM Software
Before jumping into a list of tools, know what to look for. A great ITALM solution should offer:
-
Centralized asset repository: A single dashboard to see all your hardware, software, and cloud assets in real-time.
-
Automated discovery: The ability to automatically scan your network to find and inventory all connected devices.
-
Lifecycle tracking: Functionality to track an asset through all five phases, from procurement to disposal.
-
Software license management: Tools to monitor license usage, ensure compliance, and identify savings opportunities.
-
Integration capabilities: The ability to connect with other IT systems, like Mobile Device Management (MDM), helpdesk software (ITSM), and HR platforms.
-
Reporting and analytics: Customizable dashboards and reports to measure performance, track costs, and identify trends.
-
Support for future upgrades: Flexibility and scalability to accommodate future upgrades and ongoing improvements as your needs evolve.
Top ITALM tools: A comparative look
Here are some of the leading ITAM tools available in 2025, each suited for different organizational needs.
|
Tool |
Core function |
Ideal for |
Key strength |
|---|---|---|---|
|
GroWrk |
All-in-one IT equipment & lifecycle management |
Growing, global, or remote-first organizations |
Combines global logistics, procurement, management, and sustainable disposal in one platform. |
|
ManageEngine AssetExplorer |
Comprehensive asset discovery, track software licenses for compliance and cost optimization |
Mid-sized to large enterprises |
Deep discovery capabilities and robust software license management. |
|
SolarWinds Service Desk |
Integrated ITSM and ITAM |
Organizations wanting to combine service desk and asset management |
Seamless integration between support tickets and asset data. |
|
ServiceNow |
Enterprise-grade asset and service management |
Large enterprises with complex IT environments |
Highly customizable and powerful platform that unifies IT operations. |
|
Spiceworks |
Free inventory and network monitoring |
Small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs) |
Excellent free tool for automated discovery and basic inventory management. |
Other notable tools include IBM Maximo, an enterprise asset management solution that optimizes asset performance and maintenance, as well as Sapphire, Syam Software, and SpaceRunner, each offering specialized features for different industries and use cases.
GroWrk
GroWrk focuses on managing the full lifecycle of IT assets for distributed teams on a global scale. Its services are particularly tailored for companies that need to handle the logistics of procuring, configuring, deploying, and retrieving physical hardware, such as laptops and monitors, for employees in different locations.
Key features
-
Global logistics & procurement: Handles the sourcing and shipping of IT equipment worldwide.
-
Device lifecycle management: Manages everything from pre-configuration and MDM zero-touch deployment to device retrieval and remote wiping at the end of its life.
-
Centralized platform: Offers a dashboard for tracking assets, generating reports, and creating country-specific equipment catalogs.
Pricing
Contact our sales team for a custom quote.
Pros
-
Designed specifically for the challenges of global and remote team logistics.
-
The "A La Carte" model offers flexibility with no ongoing SaaS fees.
Cons
-
Requires you to pay a small one-time fee.
ManageEngine AssetExplorer
ManageEngine AssetExplorer is a web-based IT asset management solution designed for businesses of all sizes. It helps organizations track and manage their entire IT asset lifecycle, from procurement to disposal, and includes features for license compliance, purchase order management, and maintaining a Configuration Management Database (CMDB).
Key features
-
IT Asset Lifecycle Management: Streamlines the entire lifecycle of an asset, managing vendor details, warranties, and pricing.
-
Software license & compliance management: Administers software licenses and sends alerts for expirations and renewals.
-
Purchase order & contract management: Allows users to create and manage contracts and purchase orders.
-
Configuration Management Database (CMDB): Maintains connectivity across configuration items (CIs) in the network.
Pricing
Conatct for quote.
Pros
-
Integration with service management tools makes coordination smoother and helps bridge operational gaps.
-
Automated asset discovery and inventory management capabilities provide a comprehensive view of the network.
-
Users find it assists greatly in preparing for audits by having hardware and software details in order.
Cons
-
Some users reported that the reporting features were slightly limited in relation to customization.
-
Assets based on external virtual machines may sometimes require manual intervention, breaking the automated inventory process.
-
The mobile application lacks some features present in the web version.
SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a cloud-based platform that combines IT Service Management (ITSM) with robust asset management capabilities. It is designed to help organizations streamline service operations through automation and centralized management of incidents, assets, and changes.
Key features
-
ITSM & asset management: Integrates incident, change, and problem management with comprehensive asset tracking in a single platform.
-
Asset discovery & management: Automatically discovers hardware on your network and software on your devices, providing a centralized view of your IT inventory.
-
Service portal & catalog: Offers a self-service portal for users to submit requests and access knowledge base articles.
-
Configuration Management Database (CMDB): Includes a visual CMDB and dependency mapping in higher-tier plans.
Pricing
Starts at $7 per node/per month.
Pros
-
The web and mobile app interfaces are straightforward and user-friendly, making implementation easy.
-
Offers a robust asset management feature with comprehensive asset information and auditing capabilities.
Cons
-
Users find it expensive compared to other ticketing and ITSM tools and feel it lacks scalability.
-
Lacks advanced automation, such as auto-attaching related assets to tickets, which can slow down efficiency.
-
The tool is highly tailored for IT teams, limiting its usefulness for non-IT functions like HR and finance.
ServiceNow ITAM
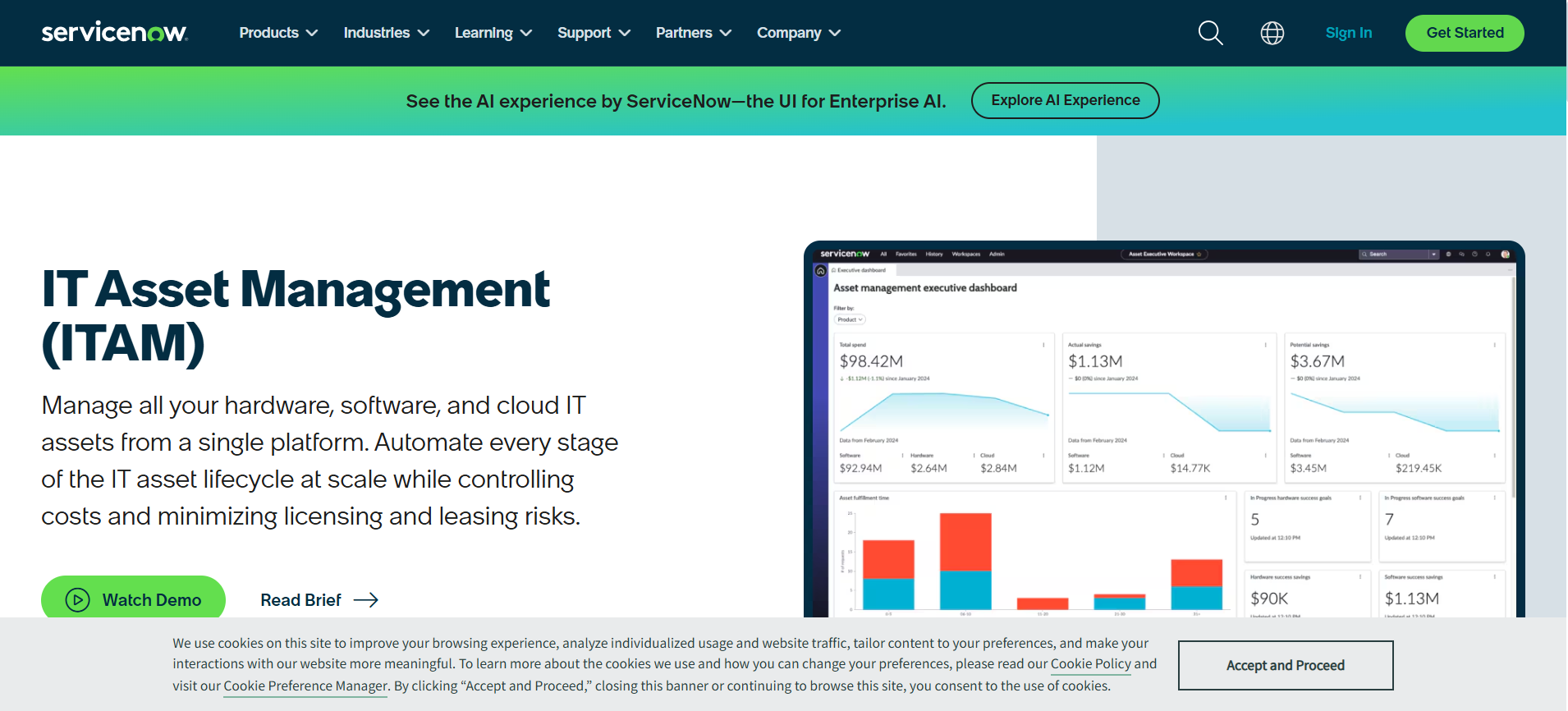
ServiceNow IT Asset Management (ITAM) is a comprehensive, cloud-based solution for managing the complete lifecycle of hardware, software, and cloud assets. It is built on the Now Platform and is designed for large enterprises that need to automate IT processes at scale, optimize costs, and minimize risks.
Key features
-
Centralized asset view: Provides a single source of truth for all IT assets, including hardware, software, and contracts.
-
End-to-end lifecycle management: Tracks and automates assets from procurement to disposal.
-
Deep ITSM integration: Works seamlessly with other ServiceNow modules like incident, change, and problem management for streamlined workflows.
-
Software license compliance: Helps track software entitlements, manage license positions, and avoid compliance issues.
Pricing
Contact for quote.
Pros
-
Highly scalable and capable of supporting large, complex enterprise environments.
-
Offers a robust ecosystem and extensive third-party integrations.
-
Automates essential processes and provides a single system of action for the enterprise.
Cons
-
The overall cost, including licensing, setup, and maintenance, is very high.
-
The platform has a steep learning curve and requires skilled experts for configuration and maintenance.
-
Users report that the platform can be complex, with slow page loading times and performance issues with large data sets.
Spiceworks
Spiceworks offers a no-frills, free-forever IT asset management system that is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses or teams with basic asset tracking demands and limited budgets. It provides core functionality like device discovery, inventory management, and help desk integration, though it is supported by ads in its free version.
Key Features
-
Device discovery & tracking: Uses an IP scanner to automatically discover devices on the network and capture details like hardware specs and installed software.
-
Asset inventory management: Allows unlimited tracking of hardware and software assets, including purchase details and warranties.
-
Help desk integration: Seamlessly integrates with its native Cloud Help Desk, linking asset data directly to support tickets.
-
Reporting: Offers flexible reporting and can export data to CSV for external analysis.
Pricing
All of Spiceworks' core plans are free forever with no limit on assets or users. The free version is ad-supported.
Pros
-
The primary advantage is its cost; it's completely free for unlimited assets and users, making it great for budget-conscious teams.
-
The integration between its asset management and help desk tools speeds up issue resolution.
-
The lack of restrictions on assets or users makes it scalable for growing teams with basic needs.
Cons
-
The platform's interface feels dated and can be clunky and difficult to navigate.
-
Lacks advanced features like geofencing, sophisticated usage alerts, or multi-stage approval workflows.
-
The free plan is funded by ads, which some users find intrusive and disruptive to workflows
Best practices for a successful ITALM program
.jpg?width=600&height=300&name=IT%20asset%20lifecycle%20management%20The%20complete%20guide%20(5).jpg)
Implementing a tool is just one step. To truly succeed, follow these best practices:
-
Establish a centralized asset repository: Your ITALM software should be the one and only source of truth. Ditch the spreadsheets.
-
Define standardized processes: Create clear, repeatable workflows for each lifecycle stage: procurement, deployment, disposal, etc.
-
Use automation: Leverage your tool's automation features for asset discovery, software updates, and regular reporting to reduce manual errors and save time.
-
Conduct regular audits: Physically or digitally audit your assets periodically to ensure your database records match reality.
-
Assign roles and responsibilities: Make someone accountable for the ITALM program's success and clearly define roles for the IT team.
Common challenges in IT Asset Lifecycle Management
Even with the right tools in place, many organizations face obstacles that limit the effectiveness of their asset lifecycle management programs. These challenges often stem from visibility gaps, outdated maintenance strategies, and the constant evolution of IT infrastructure.
Key challenges include:
-
Limited visibility: A lack of insight into asset utilization can lead to underused or forgotten assets, reducing efficiency and overall asset performance.
-
Ineffective maintenance: Inconsistent scheduling or reactive repairs increase downtime and drive up maintenance costs.
-
Budget constraints: Limited funding often restricts the ability to upgrade systems or extend asset lifespan through proactive management.
-
Technological advancements: Rapid changes in hardware and software make it difficult for IT departments to keep systems current and secure.
-
Fragmented processes: Without an integrated asset management strategy, tracking, monitoring, and maintenance can become siloed and inefficient.
-
Security risks: Outdated or untracked assets increase exposure to potential vulnerabilities across the network.
How to overcome these challenges:
-
Develop a comprehensive asset management strategy that supports the entire asset lifecycle.
-
Regularly assess and update your asset management process to match new technologies and business needs.
-
Invest in asset management software that provides centralized tracking, automation, and real-time visibility.
-
Align asset goals with broader business goals to improve efficiency, security, and long-term resilience.
By taking a structured, data-driven approach to lifecycle management, organizations can improve visibility, lower costs, and ensure that every asset continues to deliver value throughout its lifespan.
Measuring success: KPIs and metrics for ITALM
.jpg?width=600&height=300&name=IT%20asset%20lifecycle%20management%20The%20complete%20guide%20(7).jpg)
To get the most value from your asset lifecycle management program, it’s essential to track key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect both operational results and business goals. Measuring success helps ensure your asset management strategy remains effective, efficient, and adaptable.
Core KPIs and metrics to track include:
-
Asset utilization rate: Measures how efficiently assets are used to maximize performance and reduce waste.
-
Maintenance costs: Tracks total repair and servicing expenses to evaluate your maintenance strategy and identify cost-saving opportunities.
-
Asset reliability metrics: Use mean time to repair (MTTR) and mean time between failures (MTBF) to monitor asset reliability and maintenance effectiveness.
-
Incident management statistics: Analyze the frequency and resolution time of issues to uncover potential risks and improve response processes.
-
Lifecycle efficiency: Assess how well assets are performing across their entire lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
Why these metrics matter:
-
Reveal inefficiencies within your asset management process.
-
Enable data-driven decisions that extend asset lifespan and improve operational efficiency.
-
Keep your asset management efforts aligned with evolving business goals.
Regularly reviewing these KPIs helps organizations identify trends, optimize performance, and ensure every asset continues to deliver value throughout its lifecycle.
Your ITALM strategy starter checklist
Ready to get started? Use this simple checklist to begin your journey.
-
1. Assign an owner: Designate a person or team responsible for the ITALM program.
-
2. Define your scope: Decide which assets you will track first (e.g., start with laptops and software licenses).
-
3. Document your processes: Map out your current process for each of the 5 lifecycle stages.
-
4. Evaluate and select a tool: Choose an ITALM software that fits your needs and budget.
-
5. Conduct a baseline inventory: Perform an initial audit to populate your new system with accurate data.
-
6. Train your team: Ensure everyone involved understands the new processes and how to use the tool.
-
7. Monitor and improve: Regularly review your performance metrics and look for ways to optimize your program.
Why businesses choose GroWrk for IT Asset Lifecycle Management
GroWrk redefines IT Asset Lifecycle Management by combining global logistics, automation, and real-time visibility into a single unified platform. It empowers IT and operations teams to manage procurement, deployment, and recovery efficiently, without the complexity of juggling multiple vendors or tools.
Key capabilities include:
-
Global coverage: Seamless device procurement, deployment, retrieval, storage, and certified disposal in 150+ countries.
-
End-to-end automation: Automates every stage of the IT asset lifecycle, from ordering and configuration to tracking, recovery, and secure data wiping.
-
Integrated platform: Connects with HRIS, ITSM, and finance systems for unified workflows that eliminate manual tracking and email chains.
-
Security and compliance: Enforces encryption, remote lock/wipe, identity management, and SOC 2 / GDPR compliance across all endpoints.
-
Real-time visibility: Centralized dashboards deliver full oversight of asset health, ownership, and utilization for smarter decision-making.
-
Flexible, transparent pricing: Pay only for what you need with clear, per-device rates and no long-term contracts.
By aligning IT procurement, logistics, and lifecycle management under one platform, GroWrk helps organizations reduce costs, strengthen security, and scale operations globally, without adding complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the 5 stages of the asset life cycle?
The five key stages are Procurement/Planning, Deployment, Management & Maintenance, Support, and Retirement/Disposal.
How often should I conduct an asset inventory?
While practices vary, a full physical inventory is recommended at least once a year. Digital and automated systems should provide real-time data, but periodic checks are crucial to catch discrepancies.
What are the main types of IT assets?
IT assets are broadly categorized into hardware (laptops, servers), software (applications, licenses), cloud assets (virtual machines, subscriptions), and network devices (routers, switches).
What is IT asset disposition (ITAD)?
ITAD is the process of securely and sustainably disposing of obsolete or unwanted IT equipment. It is the final step in the "Retirement & Disposal" phase and focuses on data security and environmental responsibility.